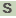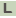フェノール分解
概要
フェノール (phenol, benzenol) は、芳香族化合物のひとつ。有機合成化学および工業品の重要な原料であるが、毒性がある。
細菌によるフェノールの好気的分解では、phenol hydroxylase (monooxygenase) によってカテコール (catechol) に変換され、 その後 オルト開裂経路 または メタ開裂経路 を経て分解される。
本項ではフェノールからカテコールへの反応について記述する。
細菌によるフェノールの好気的分解では、phenol hydroxylase (monooxygenase) によってカテコール (catechol) に変換され、 その後 オルト開裂経路 または メタ開裂経路 を経て分解される。
本項ではフェノールからカテコールへの反応について記述する。
機能に関する知見
機能を示すメカニズム
フェノール好気的分解の第一反応は、phenol hydroxylase (monooxygenase) による酸化反応である。細菌の phenol hydroxylase は 2タイプがあり、以下の特徴がある。
multicomponent monooxygenase
- alpha, beta, gamma subunits から成る (oxygenase component)
- electron transfer component (ferredoxin, ferredoxin reductase) が必須
- effector protein が必須な場合がある
- toluene/o-xylene, methane monooxygenases と相同性を示す
- 遺伝子がオペロンになっている場合が多い
single monooxygenase
- FAD-dependent
- electron transfer component (FAD reductase) が必須な場合がある
- methylphenol, chlorophenol, hydroxybenzoate monooxygenases と相同性を示す
機能を持つことが知られている生物
多くのフェノール分解菌が知られている。
multicomponent monooxygenase : Pseudomonas, Acinetobacter, Azotobacter, Ralstonia 属など
single monooxygenase : Pseudomonas, Rhodococcus, Mycobacterium, Arthrobacter 属など
multicomponent monooxygenase : Pseudomonas, Acinetobacter, Azotobacter, Ralstonia 属など
single monooxygenase : Pseudomonas, Rhodococcus, Mycobacterium, Arthrobacter 属など
関連外部リンク
- eawag-BBD: Phenol Family Degradation Pathway Map

- MetaCyc Pathway: phenol degradation I (aerobic)

MiFuPへのリンク
- NFUNC_0028 Phenol degradation
NRULE_0027 Multicomponent monooxygenase alpha subunit
NRULE_0028 Multicomponent monooxygenase beta subunit
NRULE_0029 Multicomponent monooxygenase gamma subunit
NRULE_0032 Oxygenase electron transfer component
NRULE_0033 Multicomponent monooxygenase effector protein
NRULE_0034 Putative Rieske-type ferredoxin
NRULE_0057 Ferredoxin reductase
NRULE_0083 Aromatic ring hydroxylase
NRULE_0084 Aromatic ring hydroxylase
NRULE_0101 NADH-dependent flavin reductase
(更新日 2015/07/23)